Windows 10: How to Use the Task Manager for Advanced Troubleshooting
Unlock Your PC's Potential: Mastering Windows 10 Task Manager for Peak Performance
Hey there, tech enthusiasts! Ever feel like your computer is moving at the speed of a snail in peanut butter? We've all been there, staring blankly at a frozen screen, wondering what digital gremlin is wreaking havoc on our beloved machine. Maybe you’re battling a program that’s decided to hog all the resources, or perhaps you’re just curious about what’s running in the background, silently sipping away your precious processing power. Think of your computer like a car. You wouldn't drive it without knowing how to check the engine, right? The Windows 10 Task Manager is like that engine diagnostic tool for your PC – a powerful utility that lets you peek under the hood and diagnose performance issues, manage running processes, and generally keep your system running smoothly. We're talking about a built-in superpower that’s been hiding in plain sight, ready to be unleashed. Forget expensive software and confusing jargon. This isn’t about becoming a coding wizard or a tech support guru. It’s about understanding the basics, learning a few simple tricks, and taking control of your computer's performance. This isn’t just some dry, technical manual. We’re going to make this fun, relatable, and, dare I say, even a little bit entertaining. I mean, who doesn't love a good digital mystery? So, grab your virtual magnifying glass, and let's dive into the fascinating world of Windows 10 Task Manager. Ready to transform from a frustrated user to a PC performance pro? Let's get started!
The Windows 10 Task Manager: Your Secret Weapon for a Smooth-Running PC
Let’s face it, our computers are constantly juggling a million things at once. From the software we actively use to the background processes that keep everything ticking, it's a complex digital dance. When things go wrong – when your PC slows down, freezes, or starts acting strangely – the Task Manager is your go-to tool for understanding what’s happening and taking corrective action. It’s more than just a way to close unresponsive programs; it's a comprehensive performance monitoring and management hub.
Why Should You Care About Task Manager?
Imagine you're hosting a party, and suddenly the music starts skipping, the lights flicker, and the snacks disappear at an alarming rate. You'd want to figure out what's causing the chaos, right? Task Manager helps you identify the digital culprits that are bogging down your system. It lets you:
- Identify Resource Hogs: See which applications and processes are consuming the most CPU, memory, disk, and network resources. This allows you to pinpoint the programs that are slowing down your system.
- End Unresponsive Programs: Force-quit applications that have frozen or are not responding, preventing them from further impacting your system's performance.
- Manage Startup Programs: Control which programs automatically launch when you start your computer. Disabling unnecessary startup programs can significantly improve boot times.
- Monitor Performance: Track your system's overall performance in real-time, providing valuable insights into CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network utilization.
- Troubleshoot Issues: Diagnose potential problems, such as high CPU usage by a specific process, which can indicate malware or a software conflict.
Accessing the Task Manager: Three Easy Ways
Opening the Task Manager is surprisingly simple. Here are three common methods:
- Keyboard Shortcut: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc. This is the quickest and most direct way to launch Task Manager.
- Right-Click the Taskbar: Right-click on the Windows taskbar (the bar at the bottom of your screen) and select "Task Manager" from the context menu.
- Ctrl + Alt + Delete: Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete, and then select "Task Manager" from the options presented.
Navigating the Task Manager Interface: A Guided Tour
Once you've opened the Task Manager, you'll be greeted by a window with several tabs, each providing different types of information and functionality. Let's take a closer look at each tab:
- Processes Tab: This is where you'll find a list of all the applications and background processes that are currently running on your system. It displays the name of each process, its status, and the amount of CPU, memory, disk, and network resources it's consuming. This tab is crucial for identifying resource-intensive programs.
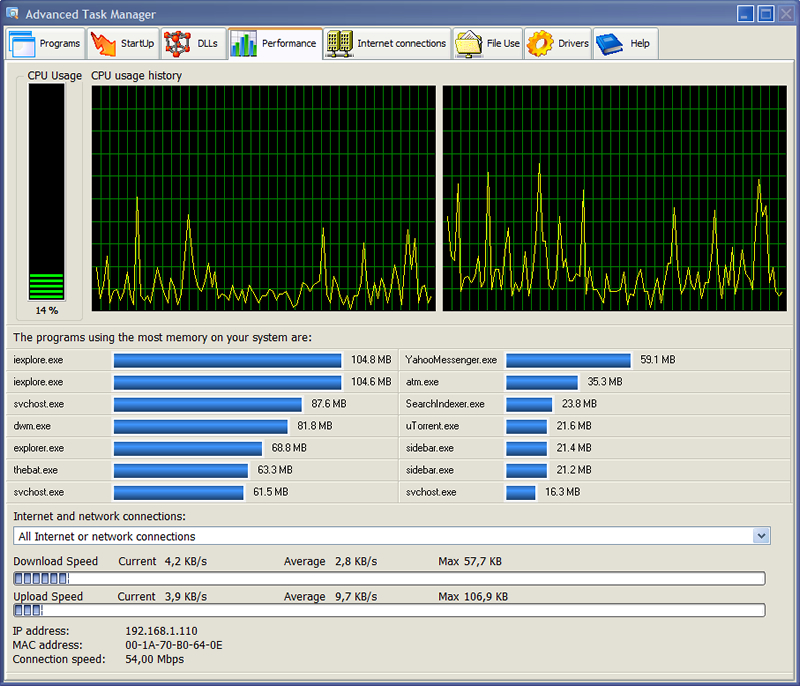
- Performance Tab: This tab provides a visual representation of your system's overall performance. You'll see graphs and charts showing CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network utilization. This is a great way to get a quick overview of your system's health and identify potential bottlenecks.
- App History Tab: This tab tracks the resource usage of Windows Store apps over time. It shows the CPU time and network usage for each app, allowing you to identify apps that are consuming excessive resources.
- Startup Tab: This tab lists the programs that automatically launch when you start your computer. You can enable or disable these programs to control which ones run in the background, improving boot times and overall system performance. Disabling unnecessary startup programs is a simple but effective way to speed up your computer.
- Users Tab: This tab displays a list of all the users currently logged in to the system, along with the resources they are using. This is useful for monitoring user activity and identifying potential performance issues related to specific user accounts.
- Details Tab: This tab provides a more detailed view of the processes running on your system. It shows the process ID (PID), user name, CPU usage, memory usage, and other technical information. This tab is primarily used by advanced users for troubleshooting specific issues.
- Services Tab: This tab lists all the Windows services running on your system. Services are background processes that perform essential tasks, such as managing network connections, printing, and system updates. You can start, stop, or restart services from this tab, but be careful, as disabling essential services can cause your system to malfunction.
Diving Deeper: Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Now that you're familiar with the Task Manager interface, let's explore some advanced troubleshooting techniques that can help you diagnose and resolve performance issues:
- Identifying Resource-Hogging Processes: The "Processes" tab is your first stop for identifying programs that are consuming excessive resources. Sort the list by CPU, Memory, Disk, or Network to quickly identify the culprits. If you see a process that's consistently using a high percentage of resources, investigate further. It could be a sign of a software bug, a malware infection, or simply a program that's not optimized for your system.
- Ending Unresponsive Programs: If an application has frozen or is not responding, you can use the Task Manager to force-quit it. Select the unresponsive program in the "Processes" tab and click the "End Task" button. This will terminate the program and free up system resources. Be aware that you may lose unsaved data when you force-quit a program.
- Managing Startup Programs for Faster Boot Times: The "Startup" tab allows you to control which programs automatically launch when you start your computer. Many programs add themselves to the startup list without your knowledge, contributing to slow boot times. Disable unnecessary startup programs to improve boot times and overall system performance. To disable a program, simply select it in the list and click the "Disable" button. Remember that disabling essential startup programs can cause your system to malfunction, so only disable programs that you know are not essential.
- Monitoring Performance in Real-Time: The "Performance" tab provides a visual representation of your system's overall performance. Pay attention to the CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network utilization graphs. If you see sustained high CPU usage, it could indicate a problem with a specific process or a malware infection. High memory consumption can lead to sluggish performance, especially if your system is running low on RAM. High disk activity can indicate that your hard drive is struggling to keep up with the demands of your system. High network utilization can indicate that your system is downloading or uploading large amounts of data, which can slow down your internet connection.
- Using the Details Tab for In-Depth Analysis: The "Details" tab provides a more detailed view of the processes running on your system. It shows the process ID (PID), user name, CPU usage, memory usage, and other technical information. This tab is primarily used by advanced users for troubleshooting specific issues. For example, you can use the PID to identify the process associated with a specific application. You can also use the "Analyze Wait Chain" feature to identify processes that are waiting for other processes to complete, which can help you diagnose performance bottlenecks.
- Checking Services: The "Services" tab lists all the Windows services running on your system. Services are background processes that perform essential tasks, such as managing network connections, printing, and system updates. You can start, stop, or restart services from this tab, but be careful, as disabling essential services can cause your system to malfunction. If you suspect that a service is causing performance issues, you can try restarting it to see if that resolves the problem.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Let's look at a few real-world examples of how the Task Manager can be used to troubleshoot performance issues:
- Case Study 1: High CPU Usage by a Mysterious Process: A user noticed that their computer was running slowly, and the Task Manager revealed that a process with a strange name was consuming a high percentage of CPU resources. After researching the process name online, they discovered that it was associated with malware. They used an anti-malware program to remove the malware, which resolved the high CPU usage and improved the system's performance.
- Case Study 2: Slow Boot Times Due to Too Many Startup Programs: A user complained that their computer took a long time to boot up. The Task Manager's "Startup" tab revealed that they had a large number of programs set to launch automatically at startup. They disabled several unnecessary startup programs, which significantly reduced boot times.
- Case Study 3: Application Freezing Due to Memory Leak: A user experienced frequent application freezes. The Task Manager's "Performance" tab showed that memory consumption was steadily increasing over time, even when the application was idle. This indicated a memory leak, a software bug that causes an application to consume more and more memory over time. The user contacted the software vendor, who released a patch to fix the memory leak.
Expert Perspectives and Future Trends
Experts agree that the Task Manager is an essential tool for diagnosing and resolving performance issues in Windows 10. As computers become more complex and software becomes more demanding, the Task Manager will continue to play a vital role in maintaining system performance.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see the Task Manager evolve to provide even more detailed performance information and advanced troubleshooting capabilities. For example, future versions of Task Manager might include:
- AI-Powered Performance Analysis: Using artificial intelligence to automatically identify performance bottlenecks and suggest solutions.
- Integration with Cloud-Based Monitoring Tools: Allowing users to monitor their system's performance remotely.
- Enhanced Security Features: Providing better protection against malware and other security threats.
By mastering the Windows 10 Task Manager, you can take control of your computer's performance, diagnose and resolve issues quickly, and keep your system running smoothly for years to come. It's a skill that will serve you well in today's increasingly digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions about the Windows 10 Task Manager:
- Question: What do I do if I accidentally end a task that's important?
Answer: If you accidentally end a task that's critical to your system's operation, your computer might become unstable or even crash. In most cases, simply restarting your computer will restore the system to a working state. Windows will automatically restart essential services and processes that were terminated. However, it's always a good idea to exercise caution and only end tasks that you're certain are not essential.
- Question: Is it safe to disable all startup programs?
Answer: No, it's not safe to disable all startup programs. Some startup programs are essential for your system's operation, such as drivers for your hardware and security software. Disabling these programs can cause your system to malfunction. Only disable startup programs that you know are not essential. If you're unsure whether a program is essential, it's best to leave it enabled.
- Question: How can I tell if a process is malware?
Answer: Identifying malware processes can be tricky, as they often try to disguise themselves as legitimate programs. However, there are a few things you can look for: Unusual process names, high resource usage, and suspicious network activity. If you suspect that a process is malware, you can research the process name online to see if other users have reported it as malicious. You can also use an anti-malware program to scan your system for malware.
- Question: What is the difference between a process and a service?
Answer: A process is a running instance of a program or application. A service is a background process that performs essential tasks, such as managing network connections, printing, and system updates. Services typically run in the background without user interaction, while processes are often associated with applications that you actively use.
In Conclusion: Unlock the Power Within
We've journeyed through the ins and outs of the Windows 10 Task Manager, transforming it from a mysterious black box into a powerful tool in your digital arsenal. We've explored its various tabs, learned how to identify resource hogs, manage startup programs, monitor performance in real-time, and even diagnose potential issues with background services. Remember, the Task Manager is your window into your PC's inner workings, allowing you to understand what's happening under the hood and take corrective action when needed.
Now that you're equipped with this knowledge, it's time to put it into practice! Take a few minutes to explore the Task Manager on your own computer. Familiarize yourself with the different tabs, experiment with ending tasks (carefully, of course!), and see if you can identify any programs that are slowing down your system. The more you use the Task Manager, the more comfortable and confident you'll become in your ability to troubleshoot performance issues and keep your PC running smoothly.
So, go forth and conquer those digital gremlins! And remember, a little bit of knowledge can go a long way in the world of technology. Are you ready to take control of your PC's performance and unlock its full potential? Happy troubleshooting!
Post a Comment for "Windows 10: How to Use the Task Manager for Advanced Troubleshooting"
Post a Comment